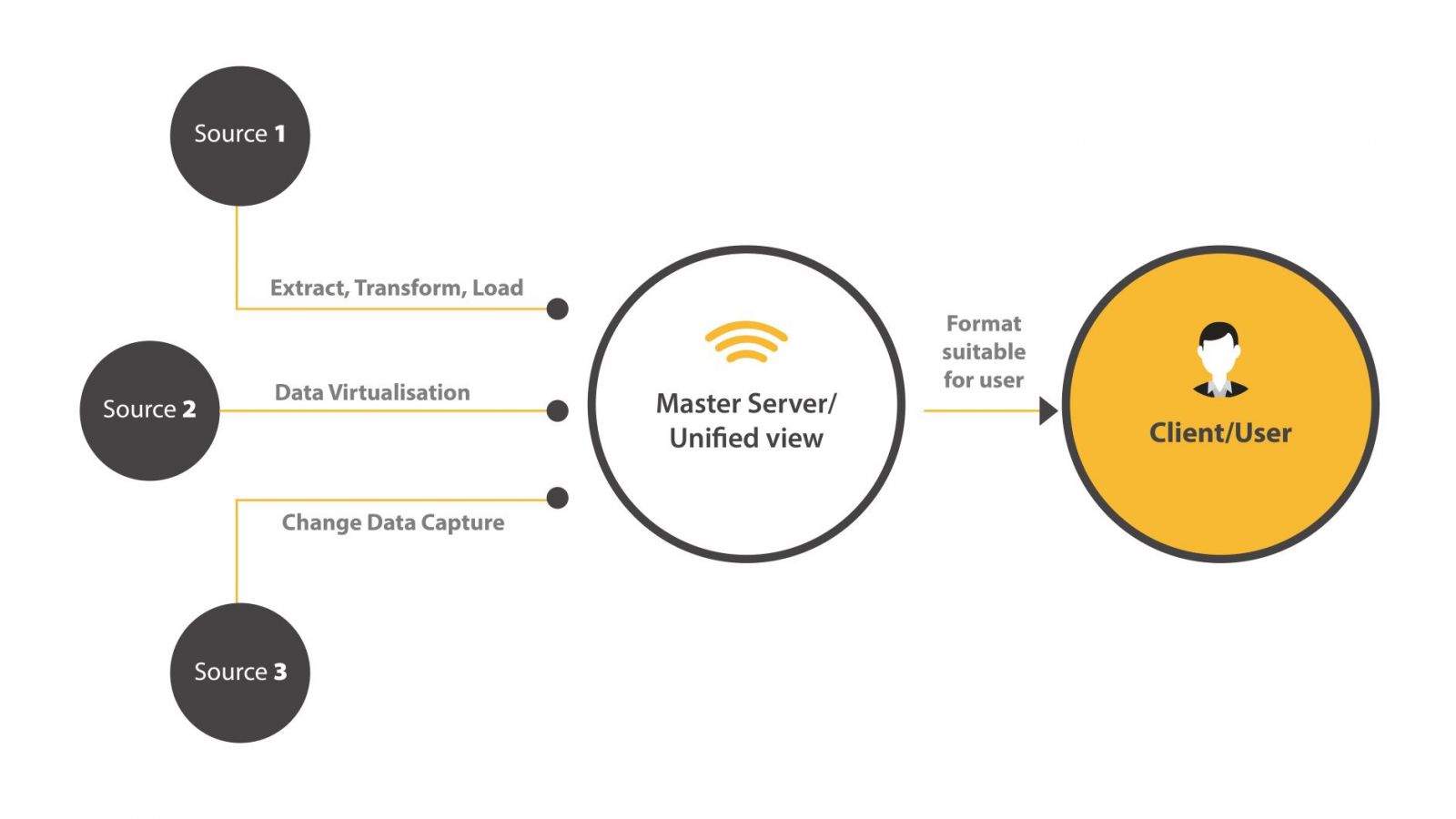
Data integration is the process of consolidating disparate data from different sources and transforming it into a unified view to provide users with more efficient and consistent access to their data. Data integration is a vital foundation element which improves the effectiveness of various data-related tasks such as data warehousing, data management, data analysis and business intelligence.
Various techniques and technologies are applied in the process to achieve an integrated view of data, including but not limited to Extract, Transform, Load (ETL), data virtualisation and change data capture.
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL): In this process, data is extracted from the sources, transformed into a suitable format for the users and loaded into the database.
Data Virtualisation: This is a more modern approach to data management where data across the enterprise is integrated to develop a unified view virtually, which means the data remains in place and doesn’t require the technical details for the data.
Change Data Capture (CDC): This is to identify or capture changes to data made in a database, synchronising them in real-time and applying it to a data warehouse.
After these integration techniques, data is then stored on a master server or in a data warehouse where users or clients can access the data. In the process, a user will send a request to the master server for data. This will initiate the server to collect data from different sources and with integration techniques, this data is consolidated in a format suitable for the user.
With this, a user can use the unified view of data for further reporting, analysis, insights and queries, achieving a more comprehensive and accurate approach for the customers.
One example of the use of data integration can be found in the healthcare industry. Integrating the data from the patients such as their personal information, past illnesses and medications which can be used to treat them more effectively. As for the industry, it means advancement to their healthcare practices and a reduction of operating costs.
Without data integration, disparate data will remain hidden and unutilised. Industries will be left unaware as to what data can do to improve their businesses and clueless about the interests and activities of their clients and customers.